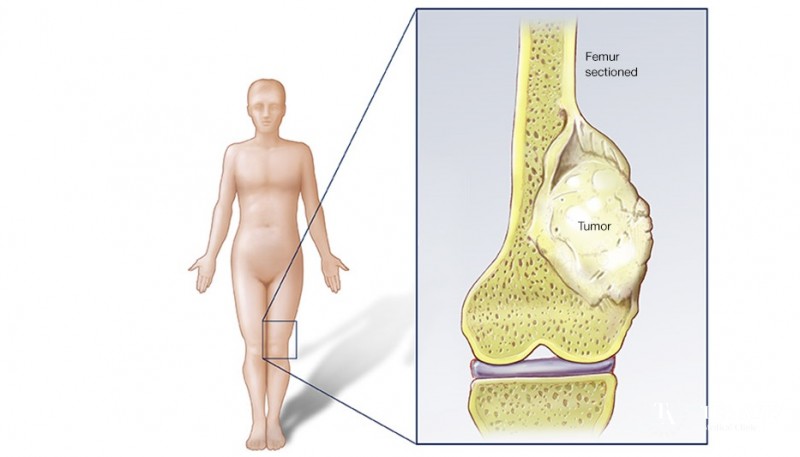
Osteosarcoma or osteogenic sarcoma – refers to an aggressive malignant tumor, the cells of which consist of bone tissue. This disease is quite common, mainly male in the second decade. Often, the neoplasm is localized in the long tubular bones of the legs and hands, as well as in the bones of the pelvis, thigh, knee, elbow and skull. The tumor can also affect soft tissue, thus pathogenic cells enter the bloodstream, and metastases manifest throughout the body.
During the disease, experts distinguish two main forms of osteosarcoma:
- Central – refer to a tumor with a high degree of malignancy.
- Superficial – is a formation with a low degree of malignancy and consists of bone or cartilage tissue. It is located close to the surface of the bone and does not destroy the cortical layer.
Symptoms of the disease
Osteosarcoma occurs in people aged 10 to 30 years. This disease occurs during the period of active bone growth. In the early stages, the tumor is very difficult to detect. Patients highlight the following symptoms:
- occurrence of limp;
- the appearance of pain at night;
- occurrence of swelling;
- fatigue, anxiety, sleep disturbance;
- weight loss and temperature.
Over time, swelling in the joint increases and movement is disrupted. It is necessary to urgently consult a doctor if there is a suspicion of osteosarcoma.
Diagnosis of pathology
Our Tel Aviv Medical Clinic employs the best oncologists who have vast experience in successfully treating various types of tumors. Our pediatric oncology department is the best in the country. Specialists help patients recover even in the most neglected cases. It is worth noting that the clinic set tariffs at the state level. Thus, you get quality services at an acceptable price. If necessary, our staff will help contact charitable foundations.
To make the correct diagnosis, qualified specialists use the following diagnostic methods:
- X-ray analysis. In the picture, the focus of bone damage will be visible.
- Biopsy. To clarify the diagnosis and correctness of therapy, it is necessary to take the material for study.
- Computed tomography. It will help to consider the tumor in more detail and its spread to other tissues.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. Allows you to determine the area of the lesion and the area of metastasis.
Then, based on the obtained data, the specialist selects the optimal therapy scheme taking into account the general state of the patient and the features of the development of pathology.
























